Gross Margin
Understand your profitability and make informed business decisions.
Gross margin determines the profitability of your business by calculating the difference between total revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS). A high gross margin indicates strong pricing power or low production costs, while a low gross margin signals potential inefficiencies or pricing challenges.
A high gross margin indicates that the company can sell its products at a higher price than it costs to produce them.
This can be a sign of strong brand recognition, customer loyalty, or other competitive advantages. On the other hand, a low gross margin may indicate that the company is struggling to compete on price, or that its production costs are too high.
Why is gross margin important?
One of the primary reasons is that it directly affects a company's net profit. When the gross margin is higher, it indicates that there is more revenue remaining after accounting for the cost of goods sold (COGS). This increased net profit can be utilized for various purposes, such as reinvesting in the business, expanding operations, or rewarding shareholders.
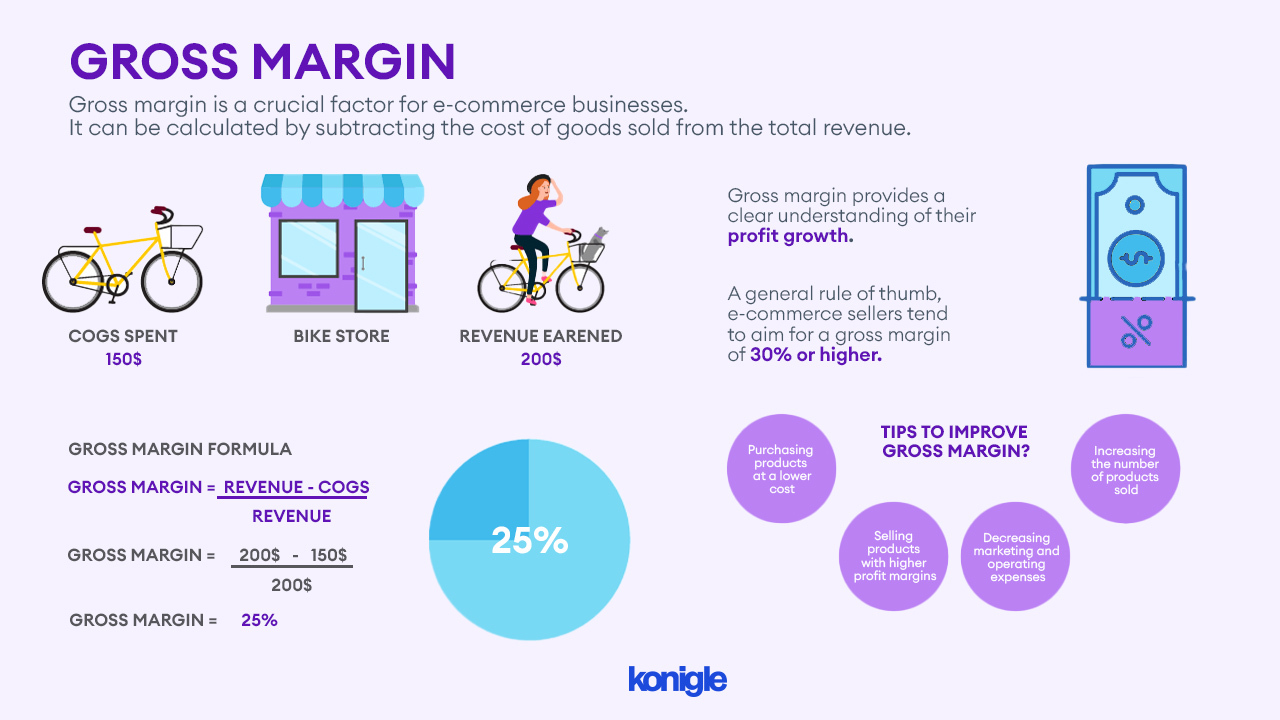
Gross margin is important for e-commerce sellers, as it provides a clear understanding of their profit growth.
By calculating gross margin, sellers can determine if they are earning enough to cover their costs and generate a profit.
A high gross margin indicates a strong financial position, while a low gross margin suggests the need for changes in the business model to improve profitability.
Additionally, the gross margin is a vital indicator of a company's pricing strategy. It allows businesses to assess if their products or services are priced correctly in relation to the production costs.
A strong gross margin indicates that a company is successfully covering its expenses and generating a satisfactory profit margin to stay competitive in the market.
What is a Good Gross Margin?
The answer to this question can vary depending on a few different factors, like the industry, product category, and business model.
However, as a general rule of thumb, e-commerce sellers tend to aim for a gross margin of 30% or higher.
How to calculate gross margin?
As you know, gross margin is a really important financial metric that helps businesses assess how profitable they are. You can calculate it by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the total revenue and then dividing the result by the total revenue. This formula will give you the gross margin as a percentage.
To determine the cost of goods sold, you'll want to take into account all the direct costs involved in producing or acquiring the goods that are eventually sold. This encompasses the expenses associated with raw materials, labor, and any other costs directly linked to the production process.
Read More: If you want to calculate profit margin, here is the best calculator to do it.
What is the gross margin formula?
The formula for calculating the gross margin percentage is as follows:
Gross margin = (total revenue - COGS) / total revenue
By analyzing the gross margin, you can get a good understanding of how efficiently your company is producing its goods or services and the pricing strategy you have in place.
A higher gross margin indicates that your company is generating more profit per unit sold, which is great!
On the other hand, a lower gross margin may suggest some inefficiencies or pricing challenges that you can work on.
Example of Gross Margin
Suppose you sell a product for $100. If the cost of goods sold for the product is $50, then the gross margin for the product is 50%.
In other words, for every $100 in revenue generated from the sale of the product, the seller earns a profit of $50.
Gross Margin vs. Gross Profit
Gross margin is often confused with gross profit, but there is a subtle difference between the two terms.
Gross profit is the amount of money your business makes after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from its total revenue.
In contrast, gross margin is expressed as a percentage and represents the proportion of total revenue that remains after deducting COGS.
Gross Margin vs. Net Margin
Gross margin is definitely an important metric to track, but it's not the only one!
Another key metric to keep an eye on is net margin, which measures the overall profitability of your business.
To calculate net margin, deduct all expenses, including COGS, marketing expenses, and operating expenses, from your total revenue.
Tips to improve Gross Margin?
There are several things that e-commerce sellers can use to improve their gross margin. These include:
- Purchasing products at a lower cost
- Selling products with higher profit margins
- Decreasing marketing and operating expenses
- Increasing the number of products sold
Conclusion
By understanding what a gross margin is, how to calculate it, and what constitutes a good gross margin, you can make informed decisions that will improve your business's profitability.